
Decongestants or medications for high blood pressure (hypertension) can cause mucus in the throat to thicken. For example, hoarseness due to excessive dryness of the throat can be a side effect of certain antihistamines, cough suppressants, diuretics and psychiatric medications. Your doctor will want to know the names of all prescription and nonprescription medications you take because some medications have side effects that can mimic the symptoms of chronic laryngitis.


Whether you drink alcohol, and how much you drink.The sensation of a lump in the throat or a dry throatĪfter reviewing your symptoms, your doctor will ask you about your lifestyle, especially:.A voice that tires easily, "breaks" or "cracks".Depending on the cause of chronic laryngitis, other symptoms can include: For the condition to be truly chronic, this hoarseness must persist for at least two weeks. The most common symptom of chronic laryngitis is hoarseness. Rarely, it can be caused by an inflammatory illness or infection directly involving the vocal cords (such as sarcoidosis or tuberculosis). Less often, chronic laryngitis can be caused by chronic sinusitis with postnasal drip. Department of Labor monitors many of these products and provides safety guidelines for handling and exposure through the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Work-related exposure to irritating chemicals or dusts - Many industrial products are suspected of causing chronic laryngitis and other respiratory problems.the sensation of having a lump in the throat (a symptom called globus),.Instead, these people may have other complaints involving the nose and throat, such as: Although some people with GERD also suffer from heartburn, indigestion and other symptoms related to the digestive tract, these symptoms are often absent in people who have chronic laryngitis because of GERD. Because acid reflux usually is worse when lying down, the hoarseness caused by GERD often is most noticeable in the morning right after awakening. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) - GERD is a disorder in which acidic fluids from the stomach flow backward (reflux) into the esophagus and throat, irritating the larynx.Drinking alcohol heavily - Alcohol causes a chemical irritation of the larynx that produces changes similar to those seen in smokers.This thickening can lower the pitch of the voice or make it sound raspy and harsh. Smoking - Cigarette smoke irritates the larynx, causing swelling and inflammation that thickens the vocal cords.Even children can develop chronic laryngitis from voice overuse or misuse, especially if they shout or strain their voices during choir practice, cheerleading or playground games. It can be an ongoing problem for people whose jobs depend on their voices, including singers, actors, telephone operators, lawyers, teachers, referees, coaches and anyone who must shout over loud noise at work (construction workers, personnel in airports and train stations, factory workers).
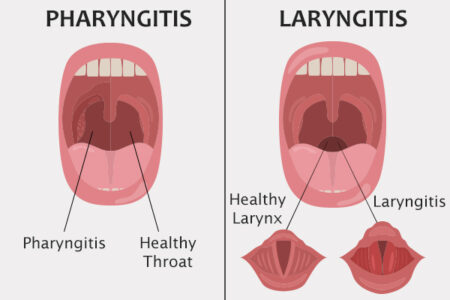
Voice abuse or misuse - This means talking too much or too loudly.It usually is painless and has no significant sign of infection.Īmong adults, the most common causes of chronic laryngitis are: Chronic laryngitis is a more persistent disorder that produces lingering hoarseness and other voice changes. In most cases, an upper respiratory tract infection causes it. Acute laryngitis typically is a brief illness producing hoarseness and a sore throat. Laryngitis occurs in two forms, acute and chronic. Laryngitis is an inflammation of the larynx, the "voice box" that contains the vocal cords in the upper portion of the neck.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
